# Build a real-time fact checker with Parallel and Cerebras
This guide demonstrates how to build a complete fact-checking application that extracts verifiable claims from any text or URL and validates them against live web sources. By the end, you'll have a streaming fact checker with a polished UI that highlights claims directly in the content as they're verified in real-time.

Fact-checking is critical to a wide range of business and academic fields. With today’s latest AI models, chips, and programmable web search, developers can quickly and easily add high-quality, ultra-fast fact-checking to virtually any workflow or application.
## Key features
- - **Two Input Modes**: Paste text directly or fetch content from any URL
- - **Claim Extraction**: LLM-powered identification of verifiable factual claims
- - **Web Verification**: Each claim is searched and validated against live web sources
- - **Real-Time Streaming**: Results stream to the UI as claims are extracted and verified
- - **Source Citations**: Every verdict includes linked source references with excerpts
- - **Visual Highlighting**: Claims are highlighted directly in the content with color-coded verdicts
## Architecture
The fact checker implements a multi-phase pipeline:
1. Content Ingestion: Accept text input or extract content from a URL
2. Claim Extraction: LLM identifies verifiable factual claims with exact source spans
3. Parallel Verification: Each claim is searched and analyzed concurrently
4. Real-Time Streaming: Results flow to the frontend via Server-Sent Events
This architecture enables sub-second feedback as claims are identified and surfaced in the UI, while verification happens in parallel to minimize total latency.
## Technology stack
- - Parallel TypeScript SDK[Parallel TypeScript SDK](https://www.npmjs.com/package/parallel-web) for Search and Extract APIs
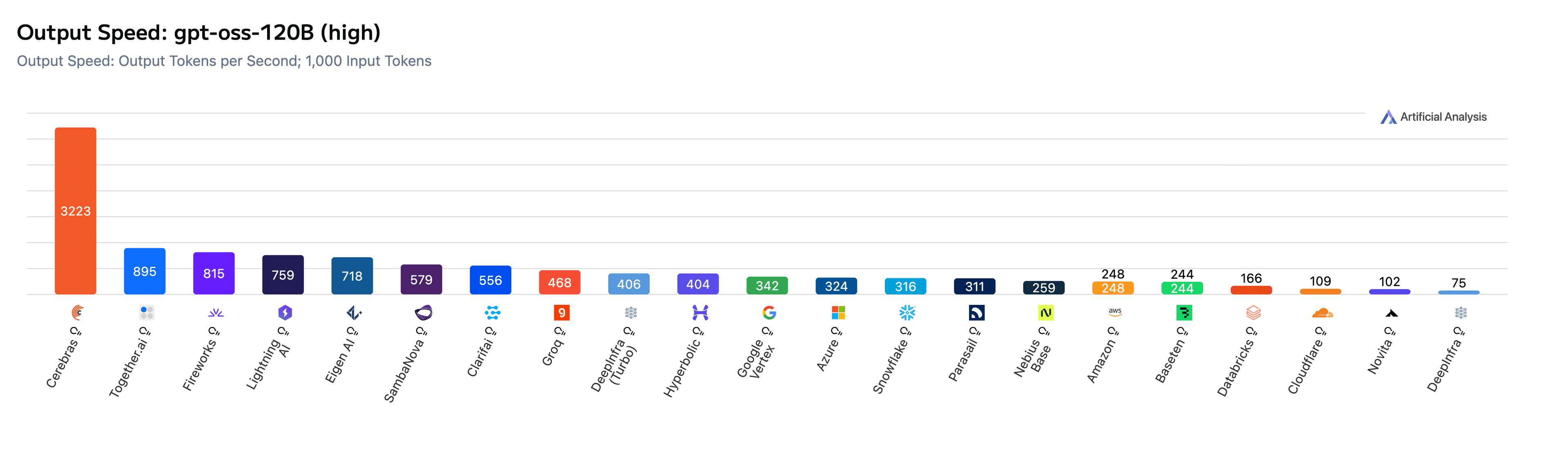
- - Cerebras[Cerebras](https://inference-docs.cerebras.ai/?utm_source=DevX&utm_campaign=parallel) for ultra-fast inference (gpt-oss-120B; up to 3000 tokens/second)
- - Vercel AI SDK for LLM [Vercel AI SDK for LLM ](https://ai-sdk.dev/docs/introduction)orchestration and streaming
- - Cloudflare Workers[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com/) (for serverless deployment
- - Pure HTML/JavaScript/CSS for the frontend
## Why this architecture
**Parallel's Search API for efficient web search**
Traditional fact-checking involves multiple steps: searching for relevant pages, scraping each page, extracting relevant content, and then analyzing it. Parallel's Search API collapses this into a single call that returns the most relevant content from multiple sources, already formatted for LLM consumption.
12345678const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({
objective: `Find reliable sources to verify or refute this claim: "${claim}"`,
search_queries: [claim],
processor: "base",
max_results: 5,
max_chars_per_result: 2000,
}``` const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({ objective: `Find reliable sources to verify or refute this claim: "${claim}"`, search_queries: [claim], processor: "base", max_results: 5, max_chars_per_result: 2000,} ``` This returns structured results with titles, URLs, and relevant excerpts, ready to feed directly into an LLM for claim analysis. This allows the app to efficiently find any mention of the claim on the web, across multiple sources, and feed the relevant excerpts surrounding the claim to an LLM for review. For example, the system can highlight that it is unsure, due to multiple reputable sources differing on the underlying claim; similarly, it can highlight that the claim is incorrect, because while several sources indicate that the claim may have some grounding, a primary source contradicts it.
### Cerebras for fast inference
Real-time fact checking places unusually strict demands on inference latency. Claims must be identified, contextualized, and evaluated quickly enough that users can see verification results appear as they read.
Cerebras powers this experience by delivering extremely high-throughput, low-latency inference. Models like **gpt-oss-120B**, hosted on Cerebras systems, is today’s leading open-weight model developed by a U.S. company, widely used for its strong reasoning and coding capabilities. Based on benchmarks from Artificial Analysis, most vendors today run gpt-oss-120B in the ~100–300 tokens/second range, reflecting typical NVIDIA H100 performance. Cerebras substantially exceed this range at ~3000 tokens/second.
For this fact checking UX, Cerebras powers the application’s ability to first, highlight the parts of a given text that are claims, almost immediately after receiving the extracted content, then analyze web search outputs related to the claim. This allows the system to make decisions about several claims almost immediately after receiving each piece of information, resulting in a responsive, interactive user experience.
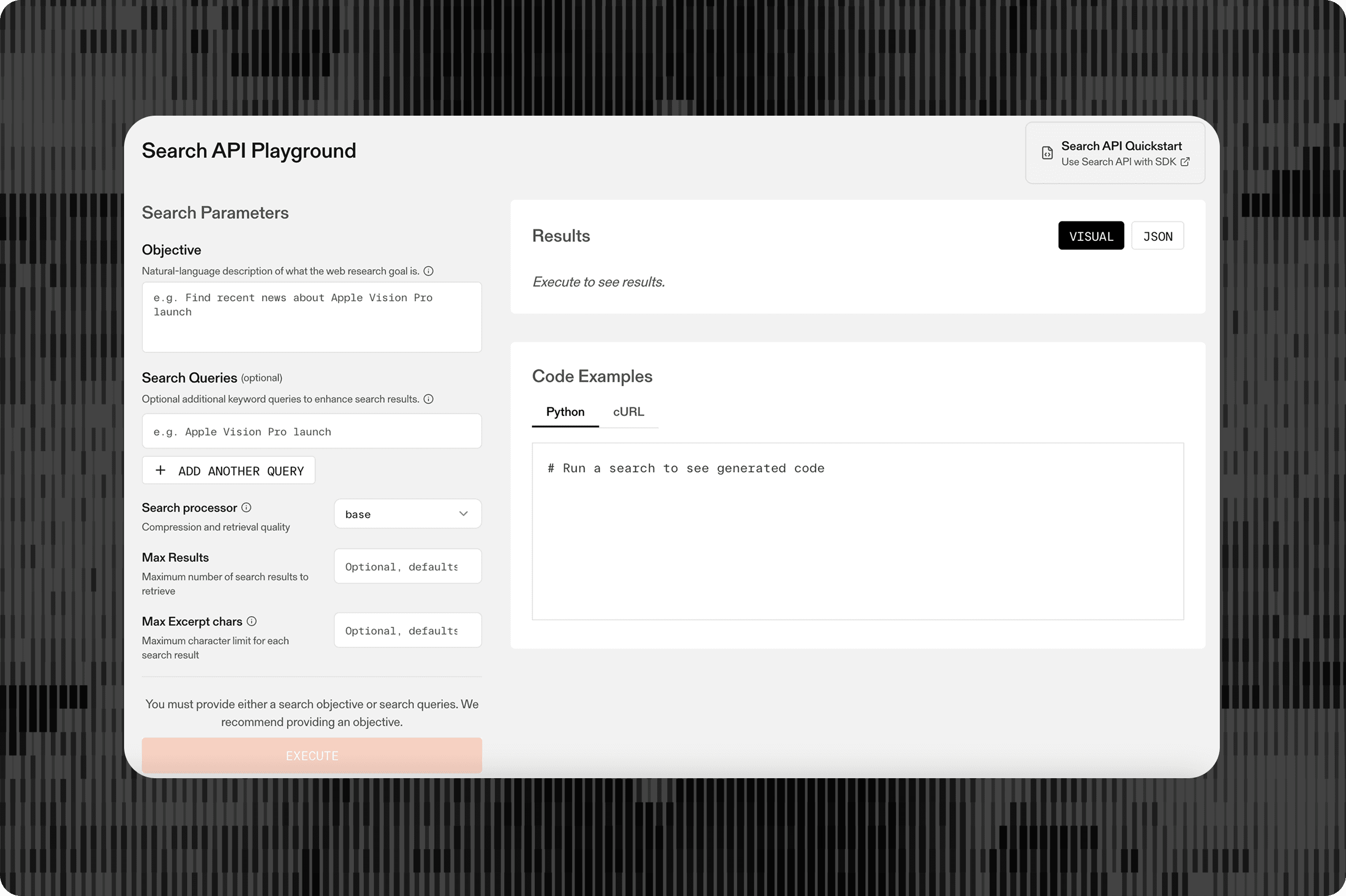
## Getting started
To start, you'll need API keys from:
- - Parallel[Parallel](https://platform.parallel.ai/) – for Search and Extract APIs
- - Cerebras[Cerebras](https://cloud.cerebras.ai/?utm_source=DevX&utm_campaign=parallel) – for LLM inference
1234567891011# Clone and install
git clone https://github.com/parallel-web/parallel-cookbook
cd typescript-recipes/parallel-fact-checker-cerebras
npm install
# Configure API keys (create .dev.vars file)
echo "PARALLEL_API_KEY=your_key_here" >> .dev.vars
echo "CEREBRAS_API_KEY=your_key_here" >> .dev.vars
# Run locally
npm run dev``` # Clone and installgit clone https://github.com/parallel-web/parallel-cookbookcd typescript-recipes/parallel-fact-checker-cerebrasnpm install # Configure API keys (create .dev.vars file)echo "PARALLEL_API_KEY=your_key_here" >> .dev.varsecho "CEREBRAS_API_KEY=your_key_here" >> .dev.vars # Run locallynpm run dev``` ## Implementation
This section walks through the key parts of the implementation. The full source is in `worker.ts`.
**1. Extracting Content from URLs**
When a user provides a URL, we use Parallel's Extract API to fetch and parse the page:
123456const extractResult = await parallel.beta.extract({
urls: [url],
objective: "Extract the main article content and key claims",
full_content: true,
});``` const extractResult = await parallel.beta.extract({ urls: [url], objective: "Extract the main article content and key claims", full_content: true,}); ``` The Extract API handles fetching, parsing, and cleaning—returning just the content, not the HTML boilerplate.
**2. Identifying Claims**
The LLM extracts verifiable claims using a structured output format. As a small prompt-tuning improvement, we ask for **exact quotes** from the source text so we can highlight them in the UI.
12345678910111213const factsResult = streamText({
model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"),
system: `Extract verifiable claims. Output format:
FACT: [EXACT QUOTE from text] ||| [claim to verify]
The quote before ||| must match the source exactly (for highlighting).`,
prompt: content,
});``` const factsResult = streamText({ model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"), system: `Extract verifiable claims. Output format: FACT: [EXACT QUOTE from text] ||| [claim to verify] The quote before ||| must match the source exactly (for highlighting).`, prompt: content, });``` As the LLM streams its response, we parse each `FACT:` line and immediately send it to the frontend—claims appear in the UI as they're discovered.
**3. Searching for Evidence**
Each claim is verified using Parallel's Search API. One call returns relevant excerpts from multiple sources:
1234567const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({
objective: `Find reliable sources to verify or refute this claim: "${fact.text}"`,
search_queries: [fact.text],
processor: "base",
max_results: 5,
max_chars_per_result: 2000,
});``` const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({ objective: `Find reliable sources to verify or refute this claim: "${fact.text}"`, search_queries: [fact.text], processor: "base", max_results: 5, max_chars_per_result: 2000, });``` The Search API is designed for LLM consumption— it returns structured excerpts, not raw HTML, saving you from building a scraping pipeline.
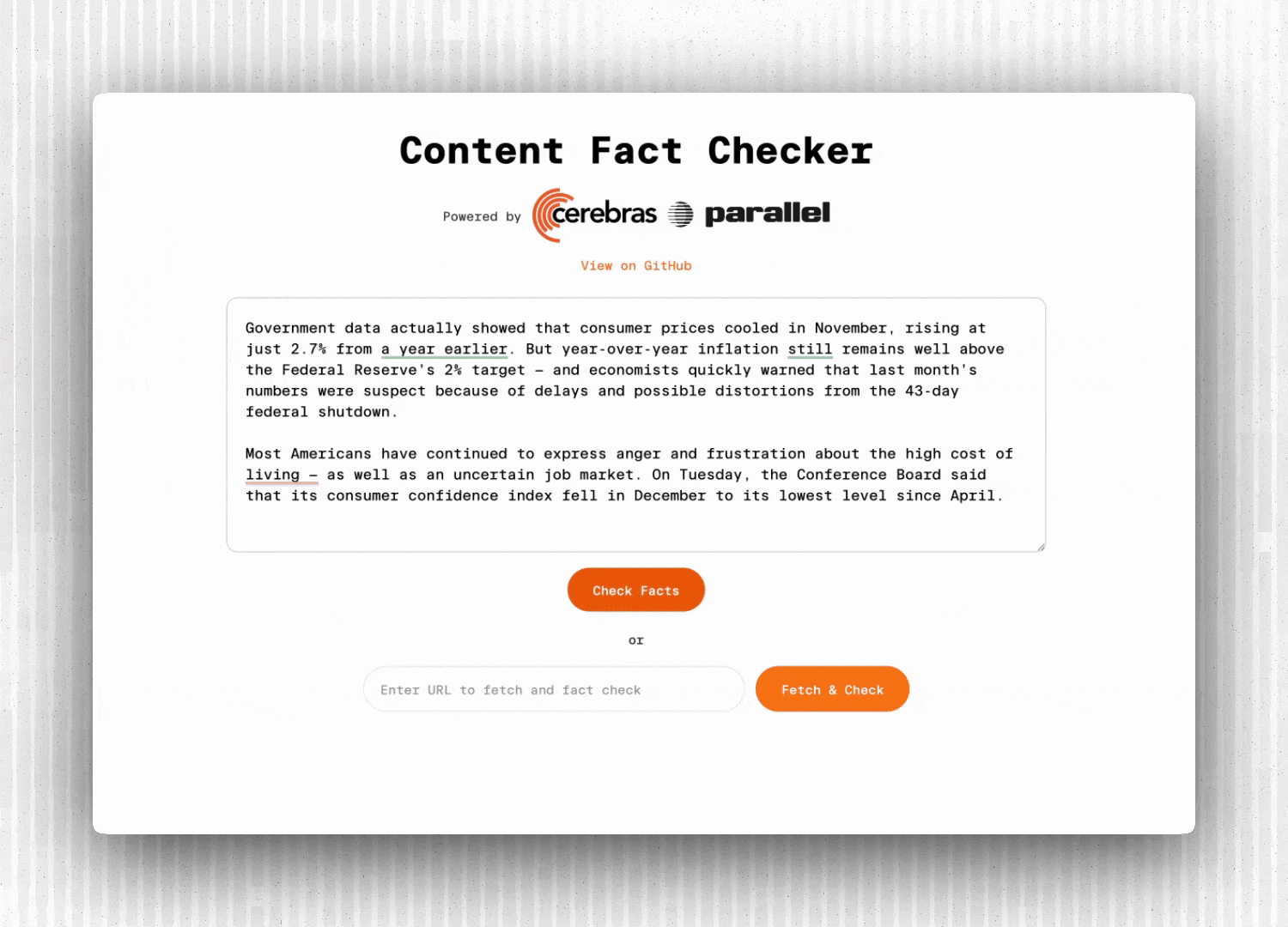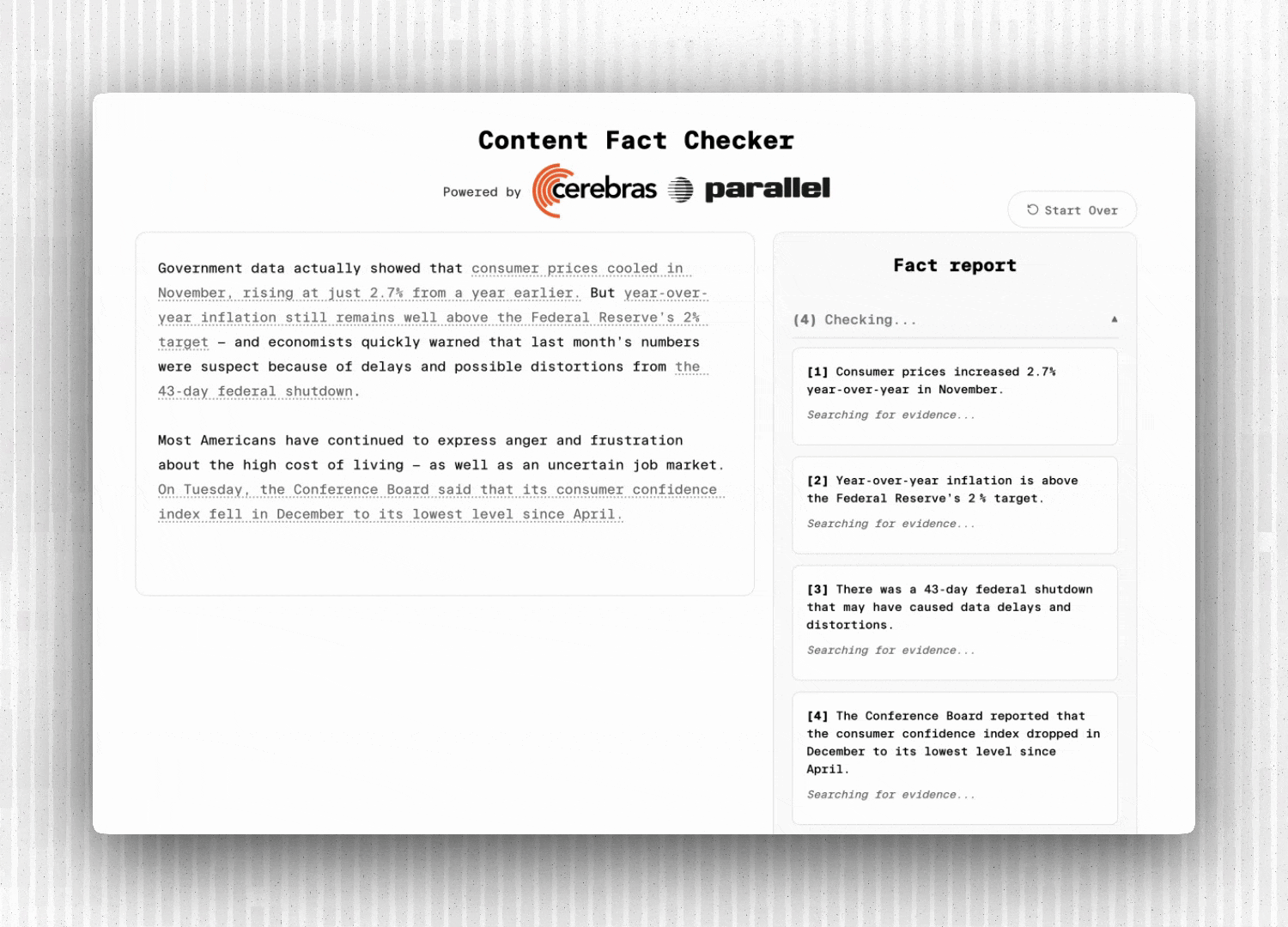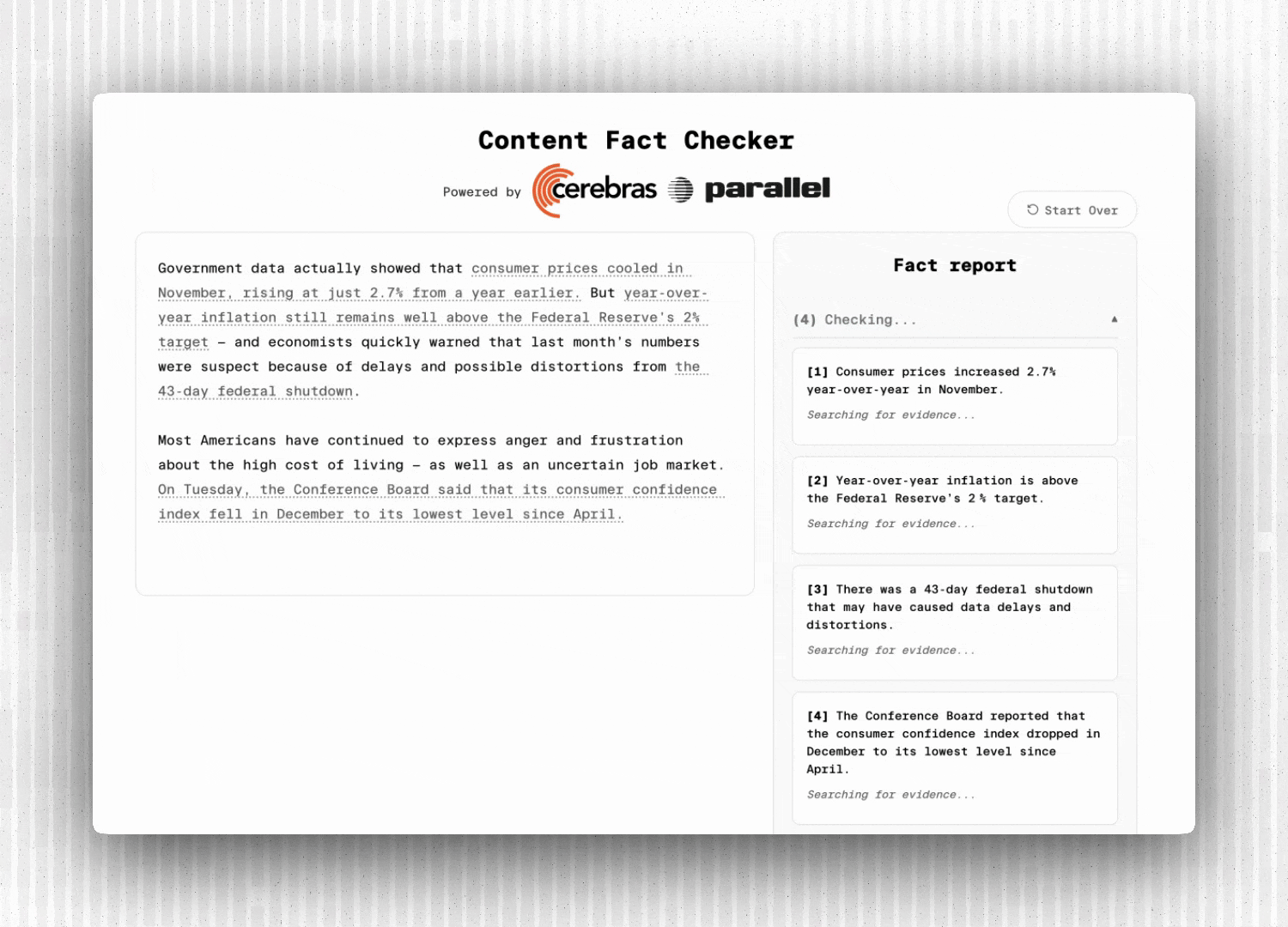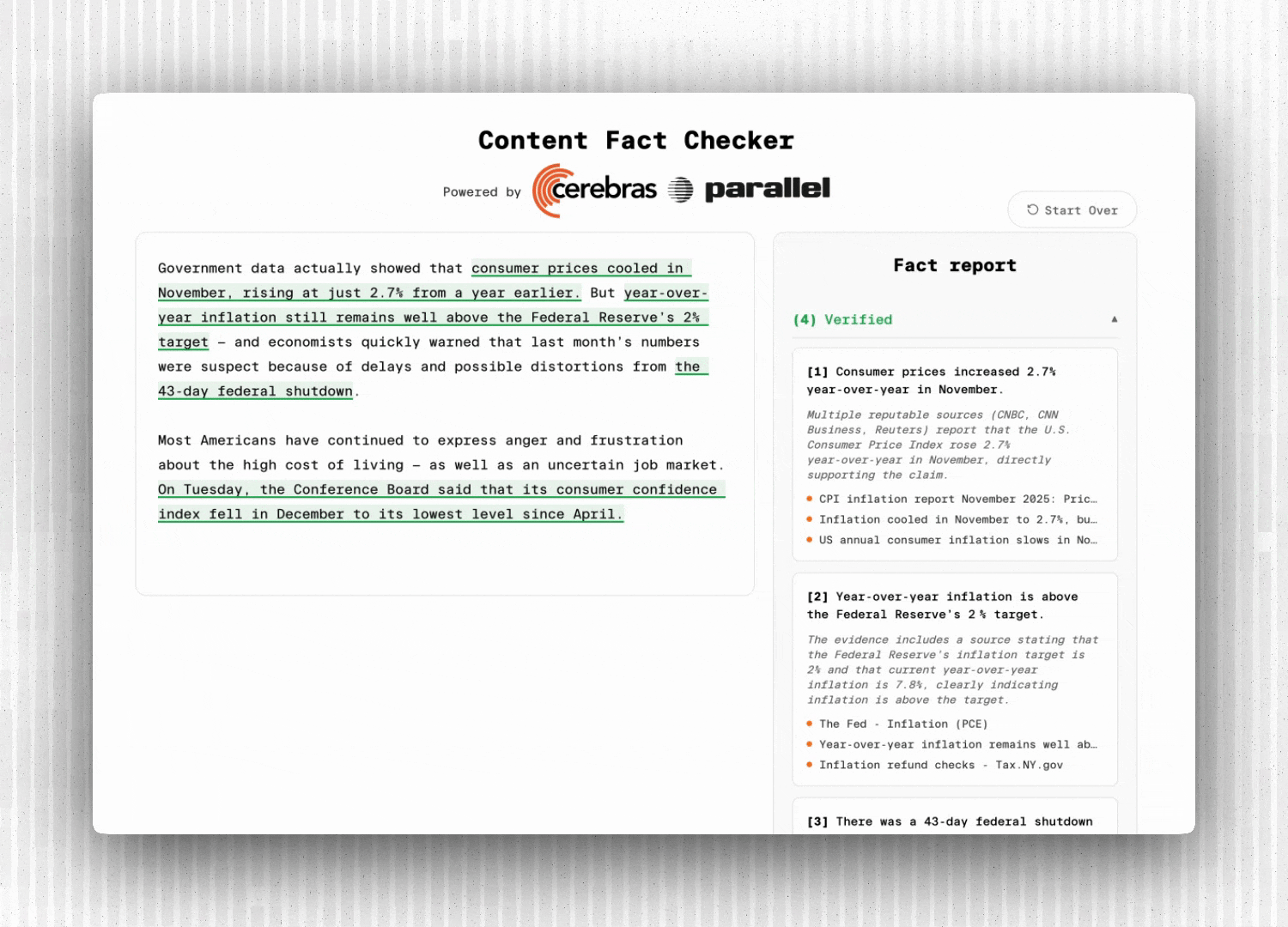
**4. Rendering Verdicts**
The LLM analyzes the search results and returns a verdict:
12345678910111213const verdict = await streamText({
model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"),
system: `Analyze evidence and respond with:
VERDICT: [VERIFIED/FALSE/UNSURE]
EXPLANATION: [1-2 sentences]`,
prompt: `Claim: "${claim}"\n\nEvidence: ${JSON.stringify(searchResults)}`,
});``` const verdict = await streamText({ model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"), system: `Analyze evidence and respond with: VERDICT: [VERIFIED/FALSE/UNSURE] EXPLANATION: [1-2 sentences]`, prompt: `Claim: "${claim}"\n\nEvidence: ${JSON.stringify(searchResults)}`, });``` We parse the verdict and send it to the frontend along with source citations.
**5. Streaming with SSE**
All results stream to the browser using Server-Sent Events. The helper is as follows:
1234567function sendSSE(controller: ReadableStreamDefaultController, data: object) {
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode(`data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}\n\n`));
}
// Usage
sendSSE(controller, { type: "fact_extracted", fact });
sendSSE(controller, { type: "fact_verdict", factId, status, explanation, references });``` function sendSSE(controller: ReadableStreamDefaultController, data: object) { controller.enqueue(encoder.encode(`data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}\n\n`));} // UsagesendSSE(controller, { type: "fact_extracted", fact });sendSSE(controller, { type: "fact_verdict", factId, status, explanation, references });``` The frontend listens for these events and updates the UI in real-time.
**6. Concurrent Verification**
Claims are verified concurrently to improve the user experience. With concurrency, several claims can be verified within the latency window of a single claim.
12345await Promise.all(
claims.map(claim => verifyFact(claim, parallel, cerebras, controller))
);``` await Promise.all( claims.map(claim => verifyFact(claim, parallel, cerebras, controller)) );``` For example, with 10 claims, this completes in ~3-5 seconds instead of 30+ seconds sequentially.
## SSE event reference
**phase**: Processing phase changed (extracting, verifying)
**content_chunk: **Streamed content chunk (URL mode)
**content_complete: **Formatted content is ready
**fact_extracted**: New claim identified (highlighted in grey on the UI)
**fact_status: **Claim status update (eg., “searching”)
**fact_verdict:** Final verdict with explanation and sources (highlighted red, orange or green)
**complete:** All processing finished
**error:** Error occurred
## Resources
- - Live Demo[Live Demo](https://oss.parallel.ai/agents/cerebras-fact-checker)
- - Source Code[Source Code](https://github.com/parallel-web/parallel-cookbook/tree/main/typescript-recipes/parallel-fact-checker-cerebras)
- - Parallel API Documentation[Parallel API Documentation](https://docs.parallel.ai/)
- - Parallel Search API[Parallel Search API](https://docs.parallel.ai/search/search-quickstart)
- - Cerebras Documentation[Cerebras Documentation](http://inference-docs.cerebras.ai/introduction?utm_source=DevX&utm_campaign=parallel)
- - Vercel AI SDK[Vercel AI SDK](https://ai-sdk.dev/)
By Parallel
January 8, 2026