# Building a Full-Stack Search Agent with Parallel and Cerebras
Build a web research agent that combines Parallel's Search API with streaming AI inference.

This guide demonstrates how to build a web research agent that combines Parallel's Search API with streaming AI inference. By the end, you'll have a complete search agent with a simple frontend that shows searches, results, and AI responses as they stream in real-time.
Complete app available here[here](https://oss.parallel.ai/agent/).
## The Architecture
The search agent we're building includes:
- - A simple search homepage
- - User-editable system prompt in config modal
- - Agent connection through Parallel Search API tool use
- - Streaming searches, search results, AI reasoning, and AI responses
- - Clean rendering of results as they arrive
Our technology stack:
- - Parallel TypeScript SDK[Parallel TypeScript SDK](https://www.npmjs.com/package/parallel-web) for the Search API
- - Vercel AI SDK[Vercel AI SDK](https://ai-sdk.dev/docs/introduction) for AI orchestration
- - Cerebras[Cerebras](https://ai-sdk.dev/providers/ai-sdk-providers/cerebras) with GPT-OSS 120B for fast responses
- - Cloudflare Workers[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com/) for deployment
## Why This Architecture Works
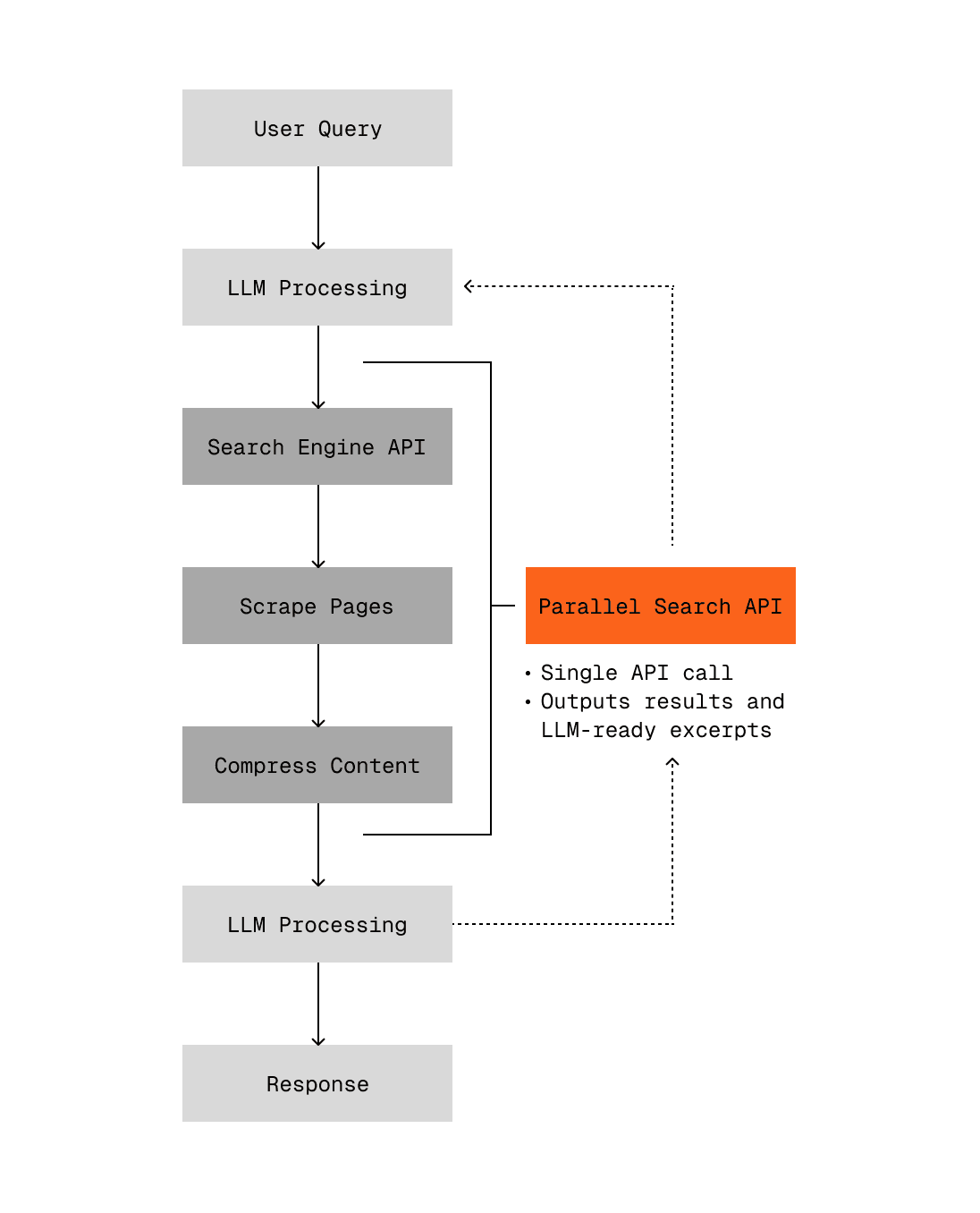
### Search API vs Traditional Agent Search Architecture
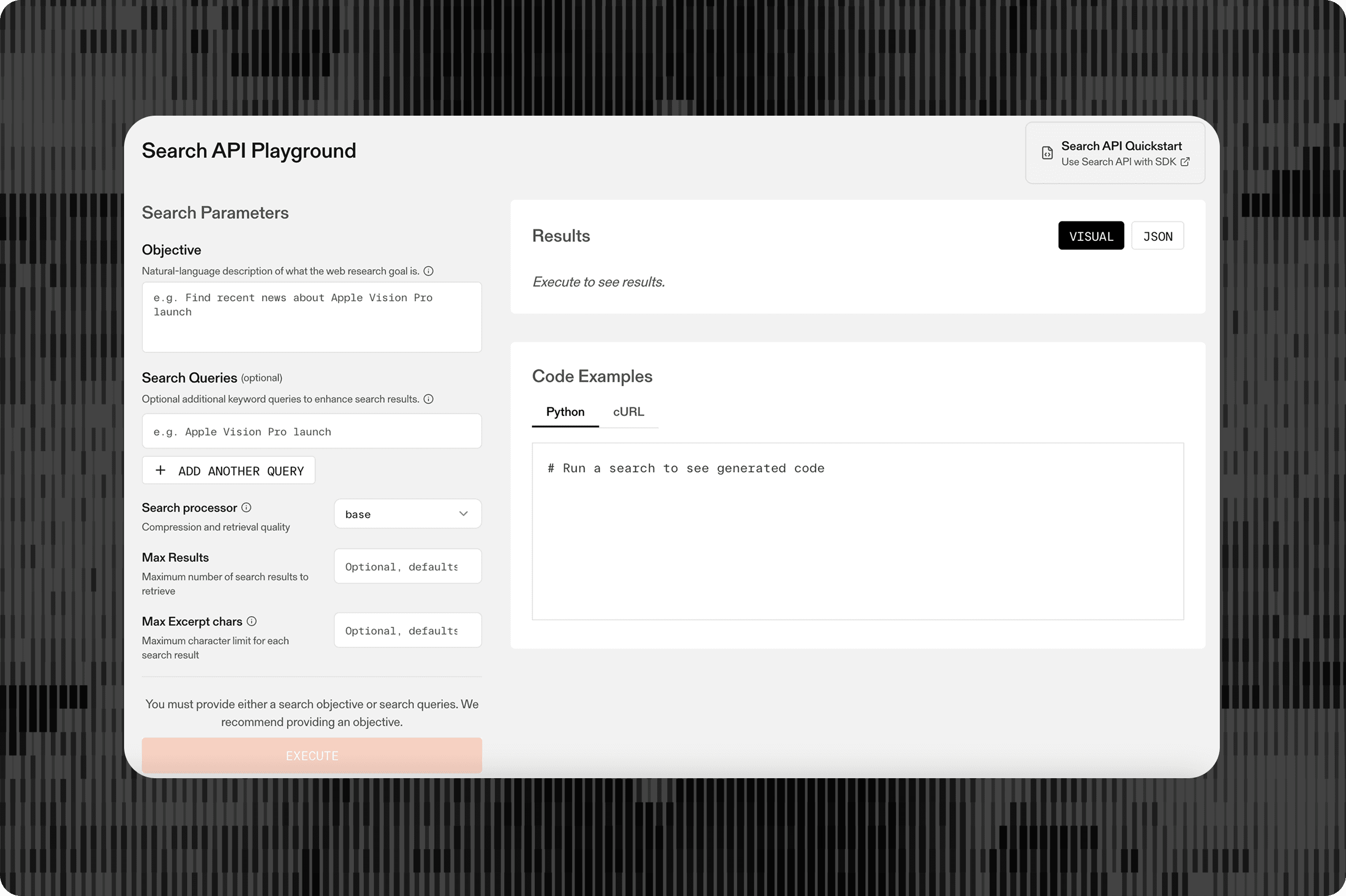
Parallel's Search API is designed for machines from first principles. The key difference from other search APIs like Exa or Tavily is that it provides all required context in a single API call. Other search approaches typically require two separate calls - one for getting the search engine results page (SERP), another for scraping the relevant pages. This traditional approach is slower and more token-heavy for the LLM.
Parallel streamlines this by finding the most relevant context from all pages immediately, returning only the relevant content to reduce context bloat. Our Search API benchmark[benchmark](/blog/search-api-benchmark) demonstrates that the Parallel Search API being used in an agentic workflow can translate to up to 20% gains in accuracy vs other Search providers.
The diagram also illustrates how the AI agent can iteratively call the Search API multiple times, allowing it to explore different angles and gather comprehensive information before providing a final response. This multi-step capability is essential for true agentic behavior.
### Choosing the Vercel AI SDK
Most AI providers ship models with built-in tool calling via /chat/completions endpoints. However, doing tool calling in a streaming fashion requires working with Server-Sent Events and multiple API round trips, which is complex to implement correctly.
The Vercel AI SDK elegantly abstracts provider-specific quirks and allows calling most providers with most of their features from a unified interface. This eliminates the need to work directly with raw API specifications and handle the back-and-forth tool calling manually.
The SDK offers multiple approaches for building this agent. While we use vanilla HTML/JavaScript for simplicity, the same backend can work with React frontends using AI SDK UI components for more sophisticated interfaces. The streaming approach we demonstrate works across different frontend frameworks, giving you flexibility in your implementation choice.
## Implementation
Now that we understand the architectural advantages, let's walk through building this search agent step by step.
### Dependencies and Setup
1npm i ai zod @ai-sdk/cerebras``` npm i ai zod @ai-sdk/cerebras``` To prevent TypeScript's "Type instantiation is excessively deep" error, zod requires a version suffix. Import the required functions:
123import { createCerebras } from "@ai-sdk/cerebras";
import { streamText, tool, stepCountIs } from "ai";
import { z } from "zod/v4";``` import { createCerebras } from "@ai-sdk/cerebras";import { streamText, tool, stepCountIs } from "ai";import { z } from "zod/v4";``` ### Defining the Search Tool
This section covers setting up the core search functionality that will power our AI agent:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839//define execution of the tool
const execute = async ({ objective }) => {
const parallel = new Parallel({
apiKey: env.PARALLEL_API_KEY,
});
const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({
objective,
search_queries: undefined,
processor: "base",
// Keep reasonable to balance context and token usage
max_results: 10,
max_chars_per_result: 1000,
});
return searchResult;
};
// Define the search tool
const searchTool = tool({
description: `# Web Search Tool
**Purpose:** Perform web searches and return LLM-friendly results.
**Usage:**
- objective: Natural-language description of your research goal (max 200 characters)
**Best Practices:**
- Be specific about what information you need
- Mention if you want recent/current data
- Keep objectives concise but descriptive`,
inputSchema: z.object({
objective: z
.string()
.describe(
"Natural-language description of your research goal (max 200 characters)"
),
}),
execute,
});``` //define execution of the toolconst execute = async ({ objective }) => { const parallel = new Parallel({ apiKey: env.PARALLEL_API_KEY, }); const searchResult = await parallel.beta.search({ objective, search_queries: undefined, processor: "base", // Keep reasonable to balance context and token usage max_results: 10, max_chars_per_result: 1000, }); return searchResult;}; // Define the search toolconst searchTool = tool({ description: `# Web Search Tool **Purpose:** Perform web searches and return LLM-friendly results. **Usage:**- objective: Natural-language description of your research goal (max 200 characters) **Best Practices:**- Be specific about what information you need- Mention if you want recent/current data- Keep objectives concise but descriptive`, inputSchema: z.object({ objective: z .string() .describe( "Natural-language description of your research goal (max 200 characters)" ), }), execute,});``` ### Key implementation choices:
- - We choose "objective" over "search_queries" because it allows for natural language description of research goals, making the tool more intuitive for the AI to use
- - The "base" processor prioritizes speed while "pro" focuses on freshness and quality - choose based on your use case requirements
- - Token limits are balanced to provide sufficient context without overwhelming the model
## Creating the Streaming Agent
Here we set up the core AI agent with multi-step reasoning capabilities:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031// Initialize Cerebras provider
const cerebras = createCerebras({
apiKey: env.CEREBRAS_API_KEY,
});
// Stream the research process
const result = streamText({
model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"),
system:
systemPrompt ||
`You are a simple search agent. Your mission is to comprehensively fulfill the user's search objective by conducting 1 up to 3 searches from different angles until you have gathered sufficient information to provide a complete answer. The current date is ${new Date(
Date.now()
)
.toISOString()
.slice(0, 10)}
**Research Philosophy:**
- Each search should explore a unique angle or aspect of the topic
- NEVER try to OPEN an article, the excerpts provided should be enough
**Key Parameters:**
- objective: Describe what you're trying to accomplish. This helps the search engine understand intent and provide relevant results.
**Output:**
After doing the searches required, write up your 'search report' that answers the initial search query. Even if you could not answer the question ensure to always provide a final report! Please do NOT use markdown tables.
`,
prompt: query,
tools: { search: searchTool },
stopWhen: stepCountIs(25),
maxOutputTokens: 20000,
});``` // Initialize Cerebras providerconst cerebras = createCerebras({ apiKey: env.CEREBRAS_API_KEY,}); // Stream the research processconst result = streamText({ model: cerebras("gpt-oss-120b"), system: systemPrompt || `You are a simple search agent. Your mission is to comprehensively fulfill the user's search objective by conducting 1 up to 3 searches from different angles until you have gathered sufficient information to provide a complete answer. The current date is ${new Date( Date.now() ) .toISOString() .slice(0, 10)} **Research Philosophy:**- Each search should explore a unique angle or aspect of the topic- NEVER try to OPEN an article, the excerpts provided should be enough **Key Parameters:**- objective: Describe what you're trying to accomplish. This helps the search engine understand intent and provide relevant results. **Output:**After doing the searches required, write up your 'search report' that answers the initial search query. Even if you could not answer the question ensure to always provide a final report! Please do NOT use markdown tables. `, prompt: query, tools: { search: searchTool }, stopWhen: stepCountIs(25), maxOutputTokens: 20000,});``` ### Important configuration details:
The stepCountIs(25) parameter allows the agent to make multiple search calls and reasoning steps, enabling thorough research across different angles before providing a comprehensive response.
The system prompt guides the agent to conduct multiple searches from different perspectives, which is crucial for comprehensive research.
12CEREBRAS_API_KEY=YOUR_KEY
PARALLEL_API_KEY=YOUR_KEY``` CEREBRAS_API_KEY=YOUR_KEYPARALLEL_API_KEY=YOUR_KEY``` ## Streaming Response Handler
This section handles the real-time streaming of agent responses to the frontend:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233// Return the streaming response
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
const stream = new ReadableStream({
async start(controller) {
try {
for await (const chunk of result.fullStream) {
const data = `data: ${JSON.stringify(chunk)}\n\n`;
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode(data));
}
controller.enqueue(encoder.encode("data: [DONE]\n\n"));
} catch (error) {
console.error("Stream error:", error);
controller.enqueue(
encoder.encode(
`data: ${JSON.stringify({
type: "error",
error: error.message,
})}\n\n`
)
);
} finally {
controller.close();
}
},
});
return new Response(stream, {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "text/event-stream",
"Cache-Control": "no-cache",
Connection: "keep-alive",
},
});``` // Return the streaming responseconst encoder = new TextEncoder();const stream = new ReadableStream({ async start(controller) { try { for await (const chunk of result.fullStream) { const data = `data: ${JSON.stringify(chunk)}\n\n`; controller.enqueue(encoder.encode(data)); } controller.enqueue(encoder.encode("data: [DONE]\n\n")); } catch (error) { console.error("Stream error:", error); controller.enqueue( encoder.encode( `data: ${JSON.stringify({ type: "error", error: error.message, })}\n\n` ) ); } finally { controller.close(); } },}); return new Response(stream, { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/event-stream", "Cache-Control": "no-cache", Connection: "keep-alive", },});``` ## Cloudflare Workers Deployment
### Configuration
1234567{
"$schema": "https://unpkg.com/wrangler@latest/config-schema.json",
"name": "web-research-agent",
"main": "worker.ts",
"compatibility_date": "2025-07-14",
"route": { "custom_domain": true, "pattern": "yourdomain.com" }
}``` { "$schema": "https://unpkg.com/wrangler@latest/config-schema.json", "name": "web-research-agent", "main": "worker.ts", "compatibility_date": "2025-07-14", "route": { "custom_domain": true, "pattern": "yourdomain.com" }}``` ## Deployment Process
Requirements:
- - Node.js
- - Wrangler CLI
- - Cloudflare account
Before deploying, submit your secrets:
1wrangler secret bulk .env``` wrangler secret bulk .env``` Deploy:
1wrangler deploy```wrangler deploy```
## Frontend Implementation
The worker also serves the frontend at the root path:
12345678import indexHtml from "./index.html";
// in your handler:
if (request.method === "GET" && url.pathname === "/") {
return new Response(indexHtml, {
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html" },
});
}``` import indexHtml from "./index.html"; // in your handler:if (request.method === "GET" && url.pathname === "/") { return new Response(indexHtml, { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html" }, });}``` ### Handling the Stream
The frontend processes the streaming responses in real-time:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113async function startResearch() {
const query = searchInput.value.trim();
if (!query) return;
showLoadingState();
currentMode = "text";
// Abort any existing request
if (abortController) {
abortController.abort();
}
abortController = new AbortController();
try {
const response = await fetch("/api/research", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query: query,
systemPrompt: currentSystemPrompt || undefined,
}),
signal: abortController.signal,
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
const reader = response.body?.getReader();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
if (!reader) {
throw new Error("No response body");
}
let buffer = "";
showResults(); // Show results interface when stream starts
while (true) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
buffer += decoder.decode(value, { stream: true });
// Process complete lines
const lines = buffer.split("\n");
buffer = lines.pop() || ""; // Keep the last incomplete line in buffer
for (const line of lines) {
if (line.startsWith("data: ")) {
const data = line.slice(6);
if (data === "[DONE]") {
return;
}
try {
const chunk = JSON.parse(data);
handleStreamChunk(chunk);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error parsing chunk:", error, data);
}
}
}
}
} catch (error) {
if (error.name === "AbortError") {
console.log("Request was aborted");
} else {
console.error("Research error:", error);
showError(`Research failed: ${error.message}`);
}
} finally {
abortController = null;
}
}
function handleStreamChunk(chunk) {
switch (chunk.type) {
case "text-delta":
if (currentMode === "reasoning") {
finalizeCurrentSection();
currentMode = "text";
}
appendText(chunk.text || "");
break;
case "reasoning-delta":
if (currentMode === "text") {
finalizeCurrentSection();
currentMode = "reasoning";
}
appendReasoning(chunk.text || "");
break;
case "tool-call":
finalizeCurrentSection();
addToolCall(chunk);
break;
case "tool-result":
addToolResult(chunk);
break;
case "error":
showError(chunk.error?.message);
break;
case "finish":
finalizeCurrentSection();
addFinishIndicator(chunk.finishReason);
console.log("Research completed with reason:", chunk.finishReason);
break;
}
}``` async function startResearch() { const query = searchInput.value.trim(); if (!query) return; showLoadingState(); currentMode = "text"; // Abort any existing request if (abortController) { abortController.abort(); } abortController = new AbortController(); try { const response = await fetch("/api/research", { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", }, body: JSON.stringify({ query: query, systemPrompt: currentSystemPrompt || undefined, }), signal: abortController.signal, }); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`); } const reader = response.body?.getReader(); const decoder = new TextDecoder(); if (!reader) { throw new Error("No response body"); } let buffer = ""; showResults(); // Show results interface when stream starts while (true) { const { done, value } = await reader.read(); if (done) break; buffer += decoder.decode(value, { stream: true }); // Process complete lines const lines = buffer.split("\n"); buffer = lines.pop() || ""; // Keep the last incomplete line in buffer for (const line of lines) { if (line.startsWith("data: ")) { const data = line.slice(6); if (data === "[DONE]") { return; } try { const chunk = JSON.parse(data); handleStreamChunk(chunk); } catch (error) { console.error("Error parsing chunk:", error, data); } } } } } catch (error) { if (error.name === "AbortError") { console.log("Request was aborted"); } else { console.error("Research error:", error); showError(`Research failed: ${error.message}`); } } finally { abortController = null; }} function handleStreamChunk(chunk) { switch (chunk.type) { case "text-delta": if (currentMode === "reasoning") { finalizeCurrentSection(); currentMode = "text"; } appendText(chunk.text || ""); break; case "reasoning-delta": if (currentMode === "text") { finalizeCurrentSection(); currentMode = "reasoning"; } appendReasoning(chunk.text || ""); break; case "tool-call": finalizeCurrentSection(); addToolCall(chunk); break; case "tool-result": addToolResult(chunk); break; case "error": showError(chunk.error?.message); break; case "finish": finalizeCurrentSection(); addFinishIndicator(chunk.finishReason); console.log("Research completed with reason:", chunk.finishReason); break; }}``` ## Styling and Dependencies
The frontend uses https://cdn.tailwindcss.com[https://cdn.tailwindcss.com](https://cdn.tailwindcss.com/) for styling, which reduces the lines needed for clean design without additional dependencies. The implementation uses regular HTML rather than React or other frameworks, making it accessible and easy to understand.
## Development Context and Resources
The complete source files provide essential context for both backend logic and frontend streaming:
Essential source files:
- - worker.ts - Complete backend implementation
- - index.html - Frontend with streaming UI
These files contain the complete TypeScript definitions and HTML implementation that are essential for understanding the full integration between the Parallel Search API and the streaming frontend.
When altering the front-end implementation, having proper Typescript context is crucial for developer experience. The AI SDK Stubs file (https://unpkg.com/ai@5.0.22/dist/index.d.ts[https://unpkg.com/ai@5.0.22/dist/index.d.ts](https://unpkg.com/ai@5.0.22/dist/index.d.ts)) was used to overcome the limited dev tooling for plain-HTML front-ends. More context can be found in SPEC.md.
## Model Considerations
The guide uses GPT-OSS 120B on Cerebras, which is one of the fastest models available and fully open source. However, there are some noted limitations. The model sometimes inaccurately stops early during search despite instructions and occasionally tries to call tools that aren't available, likely due to overfitting on training data. For production use cases, consider upgrading to better tool-calling models that don't have these quirks while maintaining similar speed. Both Groq and Cerebras provide such alternatives.
## Production Considerations
This demonstration omits several production requirements: Authentication: No user authentication is implemented
- - Rate limiting: Currently limited only by API budgets
- - Error handling: Basic error handling is shown, but could be expanded
- - Monitoring: No observability or logging beyond basic console output
Adding these features would be the next step for enterprise deployment.
The resulting agent demonstrates real-time streaming of search operations, multi-step AI reasoning with tool use, clean separation of search logic and presentation, and serverless deployment ready for scaling. The architecture shows how modern AI SDKs can simplify complex multi-step agent workflows while maintaining performance and user experience quality.
Resources:
- - Complete source code[Complete source code](https://github.com/parallel-web/parallel-cookbook/tree/main/typescript-recipes/parallel-search-agent)
- - Parallel API documentation[Parallel API documentation](https://docs.parallel.ai/search/search-quickstart)
- - Get Parallel API keys[Get Parallel API keys](https://platform.parallel.ai/)
By Parallel
September 5, 2025