# Building a real-time streaming task manager with Parallel
Build a task streaming playground that showcases Parallel's Task API with real-time Server-Sent Events (SSE).

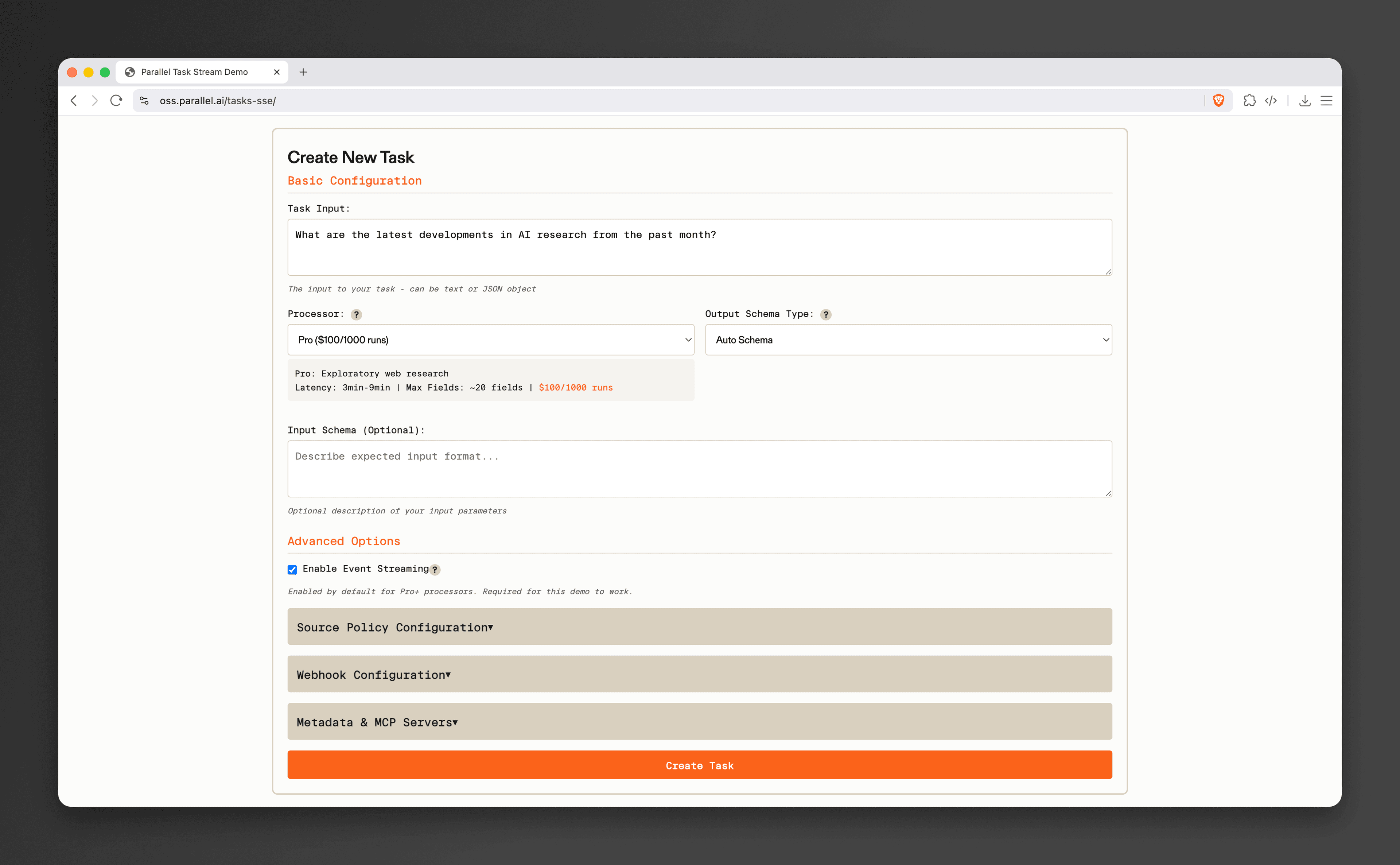
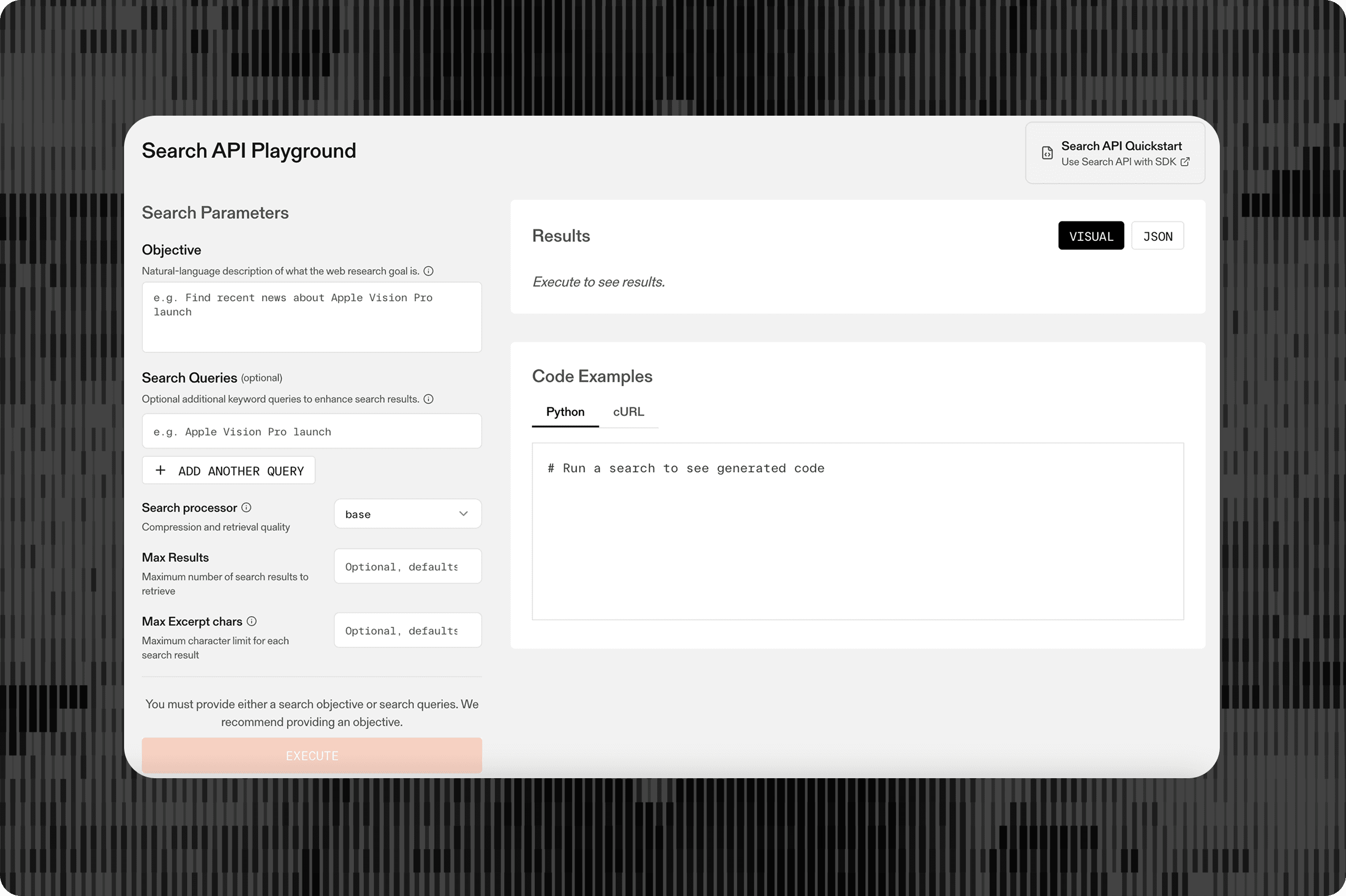
This guide demonstrates how to build a complete task streaming playground that showcases Parallel's Task API[Parallel's Task API](https://docs.parallel.ai/task-api/task-quickstart) with real-time Server-Sent Events (SSE). By the end, you'll have a full-featured application that creates tasks, streams their execution progress, and displays results as they arrive. This can be helpful for developers building with the Task API, demonstrating how to recreate the user interfaces in our Playground[Playground](https://platform.parallel.ai).
Complete demo available at: https://oss.parallel.ai/tasks-sse/[https://oss.parallel.ai/tasks-sse/](https://oss.parallel.ai/tasks-sse/)
## Key Features
- - Task Manager for All Processors: From lite ($5/1K) to ultra8x ($2400/1K)
- - Output Schemas: Text, JSON and Auto Schema
- - Source Policy: Domain inclusion and exclusion
- - Webhooks: HTTP notifications on task completion
- - Streaming events view for each Task in the Task Manager
- - OAuth flow for easy testing
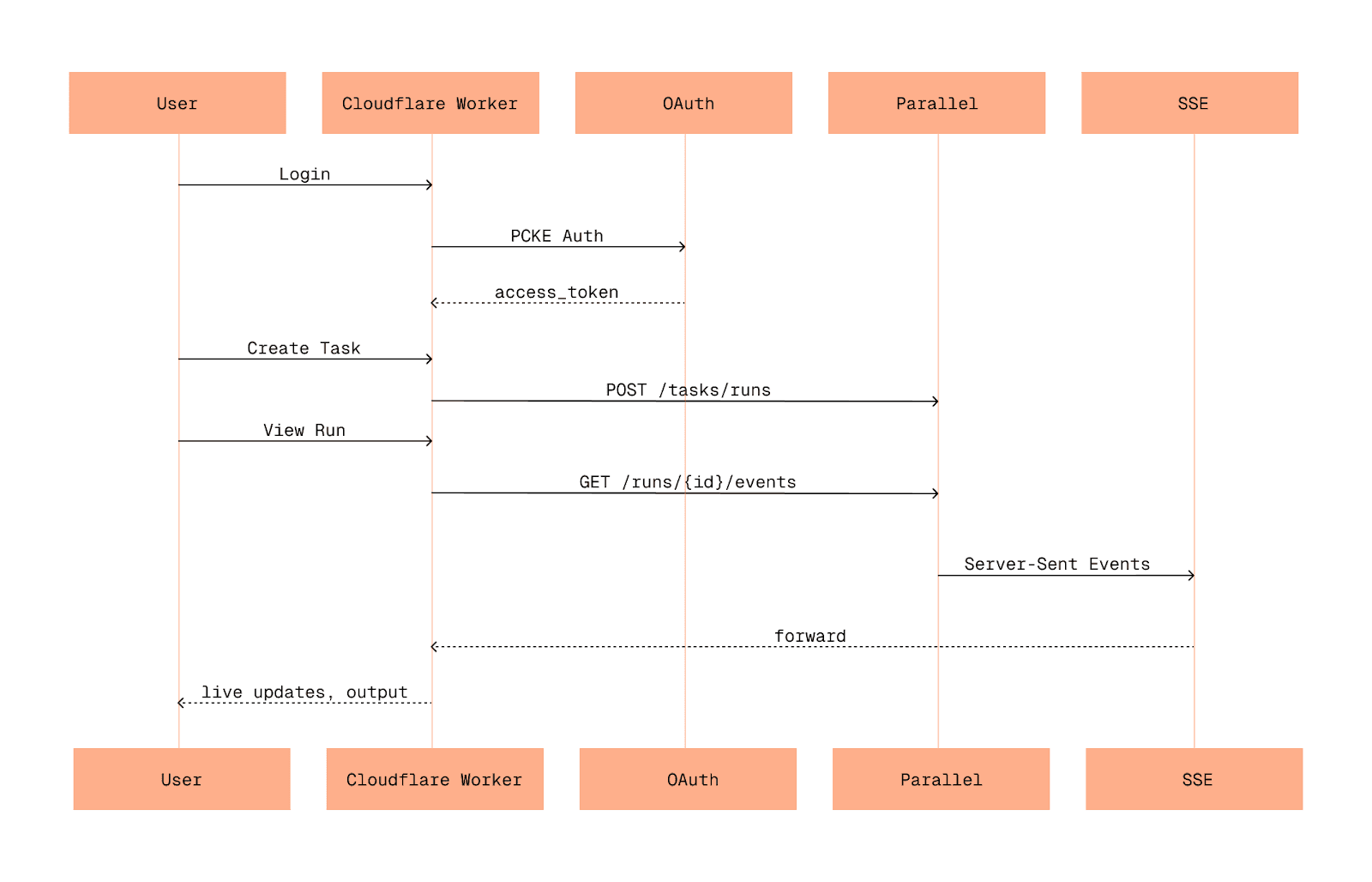
## The Architecture
The task streaming playground we're building includes:
- - OAuth2 authentication with Parallel's identity provider
- - A comprehensive task creation form supporting all processor types and output schemas
- - Real-time task progress streaming with Server-Sent Events
- - Task history management with persistent localStorage
- - Auto-reconnection for resilient streaming connections
- - Rich event visualization with progress indicators and final outputs
## Our technology stack
- - Parallel Task API for task execution
- - Parallel OAuth Provider for secure authentication
- - Server-Sent Events[Server-Sent Events](https://docs.parallel.ai/task-api/task-sse) for real-time streaming
- - Cloudflare Workers[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com/) for deployment and CORS proxying
- - Pure HTML/JavaScript/CSS for maximum compatibility
## Why this architecture
### Stateless Streaming Design
The key insight behind this implementation is that you don't need to maintain any backend state during streaming. The Parallel Task API's SSE endpoint provides the complete current state every time you connect, including:
- - All previous events that occurred before connecting
- - The latest progress statistics
- - Current task status and metadata
- - Final outputs when tasks complete
This stateless design means your backend can be incredibly simple - just a CORS proxy. All the complexity lives in the well-tested Parallel infrastructure.
### OAuth2 with PKCE Security
For production-ready authentication, we implement the complete OAuth2 flow with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange):
- Dynamic Client Registration: Register OAuth client on-demand
- PKCE Challenge: Generate cryptographically secure code challenge
- Authorization Redirect: Send user to Parallel's OAuth server
- Token Exchange: Securely exchange authorization code for access token
- Persistent Storage: Store token in localStorage for session management
This provides enterprise-grade security without requiring pre-registration of OAuth clients.
## Implementation
### Real-Time Event Streaming
Server-Sent Events (SSE) provide the real-time updates for this Task manager that helps end-users understand the progress of the Parallel Task API. This is especially helpful for longer-running processors, like Pro and above. Unlike traditional polling approaches that repeatedly ask "are you done yet?", SSE creates a persistent connection that streams updates as they happen. However, implementing SSE correctly in the browser requires handling several complex challenges.
#### Why Manual SSE Implementation?
While browsers provide a built-in `EventSource` API for SSE, it has a critical limitation: **you cannot set custom headers**. Since Parallel's API requires authentication via the `x-api-key` header, we must implement SSE manually using the Fetch API and ReadableStreams.
SSE data arrives as a continuous stream of bytes, not discrete messages. Network packets can split messages in unpredictable ways:
Our implementation handles this with a streaming buffer pattern:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223const reader = response.body.getReader();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
let buffer = '';
while (true) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
// Add new data to buffer
buffer += decoder.decode(value, { stream: true });
// Split into complete lines
const lines = buffer.split('\n');
buffer = lines.pop(); // Keep incomplete line in buffer
// Process complete lines
for (const line of lines) {
if (line.startsWith('data: ')) {
const data = JSON.parse(line.substring(6));
handleEvent(data);
}
}
}``` const reader = response.body.getReader();const decoder = new TextDecoder();let buffer = ''; while (true) { const { done, value } = await reader.read(); if (done) break; // Add new data to buffer buffer += decoder.decode(value, { stream: true }); // Split into complete lines const lines = buffer.split('\n'); buffer = lines.pop(); // Keep incomplete line in buffer // Process complete lines for (const line of lines) { if (line.startsWith('data: ')) { const data = JSON.parse(line.substring(6)); handleEvent(data); } }}``` This pattern ensures we never lose data or attempt to parse incomplete JSON, regardless of how network packets arrive.
#### Resilient Connection Management
Task execution can take anywhere from seconds to 30+ minutes. Network connections inevitably drop during long operations, so robust reconnection logic is essential:
12345678if (streamReconnectAttempts < MAX_RECONNECT_ATTEMPTS &&
currentTaskRun && ['queued', 'running'].includes(currentTaskRun.status)) {
streamReconnectAttempts++;
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`Reconnecting attempt ${streamReconnectAttempts}...`);
startStream();
}, 2000);
}``` if (streamReconnectAttempts < MAX_RECONNECT_ATTEMPTS && currentTaskRun && ['queued', 'running'].includes(currentTaskRun.status)) { streamReconnectAttempts++; setTimeout(() => { console.log(`Reconnecting attempt ${streamReconnectAttempts}...`); startStream(); }, 2000);}``` **Key resilience features:**
- - Status-based reconnection: Only retry for tasks that might still be generating events
- - Exponential backoff: 2-second delays prevent overwhelming the server
- - Attempt limiting: Prevents infinite retry loops on permanent failures
- - Stateless recovery: Each reconnection gets the complete current state
#### Understanding the Event Stream Format
Parallel's SSE stream follows the standard Server-Sent Events specification. Each event is prefixed with `data: ` and terminated with double newlines. The implementation strips the prefix and parses the JSON payload:
1234567891011for (const line of lines) {
if (line.startsWith('data: ')) {
try {
const data = JSON.parse(line.substring(6)); // Remove 'data: ' prefix
handleEvent(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error parsing event data:', error, line);
}
}
}``` for (const line of lines) { if (line.startsWith('data: ')) { try { const data = JSON.parse(line.substring(6)); // Remove 'data: ' prefix handleEvent(data); } catch (error) { console.error('Error parsing event data:', error, line); } }} ``` #### Event Type Taxonomy
The stream delivers several categories of events, each serving a different purpose:
- - `task_run.state`: Core lifecycle events (queued → running → completed/failed)
- - `task_run.progress_stats`: Quantitative metrics (sources found, pages read, tokens used)
- - `task_run.progress_msg.*`: Qualitative updates with timestamped reasoning steps
- - `task_run.progress_msg.reasoning`: AI thought process
- - `task_run.progress_msg.search`: Search query generation
- - `task_run.progress_msg.analysis`: Content analysis steps
- - `error`: Exception conditions with detailed error messages
This rich event taxonomy enables granular UI updates - progress bars for stats, reasoning displays for AI thinking, and error handling for failures.
#### Event Visualization and UI
The frontend renders different event types with appropriate styling:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041function handleEvent(data) {
console.log(`event [${data.type}]`, data);
let eventHtml = '';
let eventClass = '';
switch (data.type) {
case 'task_run.state':
eventClass = 'state';
eventHtml = `
<div class="event-type">TASK STATE</div>
<div class="event-message">
Status: <span class="status ${data.run.status}">${data.run.status}</span>
${data.run.error ? `<br><span class="error">Error: ${data.run.error.message}</span>` : ''}
</div>
`;
// Display final output
if (data.output) {
const outputHtml = formatOutput(data.output);
eventHtml += `<div class="output-section">
<strong>Final Output:</strong>
${outputHtml}
</div>`;
}
break;
case 'task_run.progress_stats':
eventClass = 'progress-stats';
const stats = data.source_stats;
eventHtml = `
<div class="event-type">PROGRESS STATS</div>
<div class="progress-stats">
<div class="stat">Sources Considered: ${stats.num_sources_considered || 'N/A'}</div>
<div class="stat">Sources Read: ${stats.num_sources_read || 'N/A'}</div>
</div>
${stats.sources_read_sample ? `
<div style="margin-top: 10px;">
<strong>Sample Sources:</strong>
<ul style="margin-top: 5px; margin-left: 20px;">
${stats.sources_read_sample.slice(0, 3).map(url => ``` function handleEvent(data) { console.log(`event [${data.type}]`, data); let eventHtml = ''; let eventClass = ''; switch (data.type) { case 'task_run.state': eventClass = 'state'; eventHtml = ` <div class="event-type">TASK STATE</div> <div class="event-message"> Status: <span class="status ${data.run.status}">${data.run.status}</span> ${data.run.error ? `<br><span class="error">Error: ${data.run.error.message}</span>` : ''} </div> `; // Display final output if (data.output) { const outputHtml = formatOutput(data.output); eventHtml += `<div class="output-section"> <strong>Final Output:</strong> ${outputHtml} </div>`; } break; case 'task_run.progress_stats': eventClass = 'progress-stats'; const stats = data.source_stats; eventHtml = ` <div class="event-type">PROGRESS STATS</div> <div class="progress-stats"> <div class="stat">Sources Considered: ${stats.num_sources_considered || 'N/A'}</div> <div class="stat">Sources Read: ${stats.num_sources_read || 'N/A'}</div> </div> ${stats.sources_read_sample ? ` <div style="margin-top: 10px;"> <strong>Sample Sources:</strong> <ul style="margin-top: 5px; margin-left: 20px;"> ${stats.sources_read_sample.slice(0, 3).map(url => ``` ### CORS Proxy Worker
A simple worker solves a fundamental web security challenge. Modern browsers implement the Same-Origin Policy, which prevents JavaScript running on `yourdomain.com` from making direct API calls to `api.parallel.ai`. This security feature protects users from malicious websites, but it also blocks legitimate applications from accessing external APIs.
Traditional solutions involve building a full backend API server that handles authentication, request validation, and response transformation. Instead, we use a much simpler proxy pattern that acts as a transparent middleman:
- - Path Rewriting: `/tasks-sse/api/v1/tasks/runs` becomes `https://api.parallel.ai/v1/tasks/runs`
- - Header Preservation: All original headers (including `x-api-key`) are forwarded
- - CORS Headers: Added to all responses to enable browser access
- - Static Serving: The same worker serves the HTML frontend
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263// @ts-ignore
import indexHtml from "./index.html";
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
const url = new URL(request.url);
// Serve the frontend
if (url.pathname === "/tasks-sse/") {
return new Response(indexHtml, {
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf8" },
});
}
// Proxy Parallel API requests
if (url.pathname.startsWith("/tasks-sse/api/")) {
// Remove /api prefix and forward to api.parallel.ai
const targetPath = url.pathname.replace("/tasks-sse/api", "");
const targetUrl = `https://api.parallel.ai${targetPath}${url.search}`;
// Clone the request but change the URL
const modifiedRequest = new Request(targetUrl, {
method: request.method,
headers: request.headers,
body: request.body,
});
// Forward the request
const response = await fetch(modifiedRequest);
// Clone the response to modify headers
const modifiedResponse = new Response(response.body, {
status: response.status,
statusText: response.statusText,
headers: {
...Object.fromEntries(response.headers),
// Add CORS headers
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS",
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "*",
},
});
return modifiedResponse;
}
// Handle preflight requests
if (request.method === "OPTIONS") {
return new Response(null, {
headers: {
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS",
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "*",
},
});
}
return new Response(null, {
status: 302,
headers: { Location: "/tasks-sse/" },
});
},
};``` // @ts-ignoreimport indexHtml from "./index.html"; export default { async fetch(request, env, ctx) { const url = new URL(request.url); // Serve the frontend if (url.pathname === "/tasks-sse/") { return new Response(indexHtml, { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf8" }, }); } // Proxy Parallel API requests if (url.pathname.startsWith("/tasks-sse/api/")) { // Remove /api prefix and forward to api.parallel.ai const targetPath = url.pathname.replace("/tasks-sse/api", ""); const targetUrl = `https://api.parallel.ai${targetPath}${url.search}`; // Clone the request but change the URL const modifiedRequest = new Request(targetUrl, { method: request.method, headers: request.headers, body: request.body, }); // Forward the request const response = await fetch(modifiedRequest); // Clone the response to modify headers const modifiedResponse = new Response(response.body, { status: response.status, statusText: response.statusText, headers: { ...Object.fromEntries(response.headers), // Add CORS headers "Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*", "Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS", "Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "*", }, }); return modifiedResponse; } // Handle preflight requests if (request.method === "OPTIONS") { return new Response(null, { headers: { "Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*", "Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS", "Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "*", }, }); } return new Response(null, { status: 302, headers: { Location: "/tasks-sse/" }, }); },};``` ### OAuth Authentication
The OAuth flow implementation handles dynamic client registration, as well as the complete PKCE security protocol:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647async function startOAuth() {
try {
// Register client dynamically
const reg = await fetch("https://platform.parallel.ai/getKeys/register", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({
redirect_uris: [window.location.origin + window.location.pathname]
}),
});
const { client_id } = await reg.json();
// Generate PKCE challenge
const cv = btoa(crypto.getRandomValues(new Uint8Array(32))).replace(
/[+/=]/g, (m) => ({ "+": "-", "/": "_", "=": "" }[m])
);
localStorage.setItem('code_verifier', cv);
const cc = btoa(
String.fromCharCode(
...new Uint8Array(
await crypto.subtle.digest(
"SHA-256",
new TextEncoder().encode(cv)
)
)
)
).replace(/[+/=]/g, (m) => ({ "+": "-", "/": "_", "=": "" }[m]));
// Redirect to OAuth server
const url = new URL("https://platform.parallel.ai/getKeys/authorize");
Object.entries({
client_id,
redirect_uri: window.location.origin + window.location.pathname,
response_type: "code",
scope: "api",
code_challenge: cc,
code_challenge_method: "S256",
state: Math.random().toString(36).substring(7)
}).forEach(([k, v]) => url.searchParams.set(k, v));
window.location.href = url;
} catch (error) {
alert('OAuth error: ' + error.message);
}
}``` async function startOAuth() { try { // Register client dynamically const reg = await fetch("https://platform.parallel.ai/getKeys/register", { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify({ redirect_uris: [window.location.origin + window.location.pathname] }), }); const { client_id } = await reg.json(); // Generate PKCE challenge const cv = btoa(crypto.getRandomValues(new Uint8Array(32))).replace( /[+/=]/g, (m) => ({ "+": "-", "/": "_", "=": "" }[m]) ); localStorage.setItem('code_verifier', cv); const cc = btoa( String.fromCharCode( ...new Uint8Array( await crypto.subtle.digest( "SHA-256", new TextEncoder().encode(cv) ) ) ) ).replace(/[+/=]/g, (m) => ({ "+": "-", "/": "_", "=": "" }[m])); // Redirect to OAuth server const url = new URL("https://platform.parallel.ai/getKeys/authorize"); Object.entries({ client_id, redirect_uri: window.location.origin + window.location.pathname, response_type: "code", scope: "api", code_challenge: cc, code_challenge_method: "S256", state: Math.random().toString(36).substring(7) }).forEach(([k, v]) => url.searchParams.set(k, v)); window.location.href = url; } catch (error) { alert('OAuth error: ' + error.message); }}``` ## Resources
- - App Source Code[App Source Code](https://github.com/parallel-web/parallel-cookbook/tree/main/typescript-recipes/parallel-tasks-sse)
- - Live App Example[Live App Example](https://oss.parallel.ai/tasks-sse/)
- - Parallel SSE Documentation[Parallel SSE Documentation](https://docs.parallel.ai/task-api/task-sse)
By Parallel
October 6, 2025