# Understanding llms.txt: The new standard for AI-friendly website optimization
AI systems now consume web content as frequently as humans do, but they process information fundamentally differently— they work with tokens and context windows rather than visual layouts and navigation menus. The llms.txt file is a plain text markdown document placed at your website's root that provides large language models with a structured map of your most important content, helping them locate and understand your key resources without wading through HTML complexity. This guide explains what llms.txt is, how it works, why it differs from robots.txt and sitemaps, and how to implement it effectively— plus what the standard means for AI agents accessing web data at scale.

## **What Is llms.txt?**
The llms.txt file is a plain text markdown document that sits at the root of your website—at yourdomain.com/llms.txt—giving large language models (LLMs) a structured map of your most important content. While traditional search engines parse HTML and follow links, AI systems work with tokens and context windows, which makes navigating complex website architectures a different challenge entirely.
Here's how it works: you create a markdown file with your site name as an H1 heading, add a brief description in blockquote format, then organize links to your key pages with short explanations of what each contains. The format looks something like this:
12345678910111213# Parallel Web Systems
> This is the agent-friendly navigation document (llms.txt) for all public Parallel content. It is comprised of all public content from the main website (including all blog-posts), the docs, and a few resources from our SDKs.
Parallel is a Enterprise Deep Research Product with APIs for performing Web Search Tasks at scale.
## Main Website
- [About Parallel](/about.md): The web's second user. Building web search and infrastructure for AIs.
- [Parallel Web Systems](/articles.md): Parallel builds web data and APIs for AI agents—turning web search and knowledge tasks into programmable, enterprise-ready infrastructure.
- [AI Web Search and AI Deep Research for Sales Enrichment](/articles/ai-web-enrichment-for-sales.md): Deep research AI sales web enrichment using AI search APIs. Create custom prospect intelligence beyond Apollo/ZoomInfo with automated data gathering tools.
...``` # Parallel Web Systems > This is the agent-friendly navigation document (llms.txt) for all public Parallel content. It is comprised of all public content from the main website (including all blog-posts), the docs, and a few resources from our SDKs. Parallel is a Enterprise Deep Research Product with APIs for performing Web Search Tasks at scale. ## Main Website - [About Parallel](/about.md): The web's second user. Building web search and infrastructure for AIs.- [Parallel Web Systems](/articles.md): Parallel builds web data and APIs for AI agents—turning web search and knowledge tasks into programmable, enterprise-ready infrastructure.- [AI Web Search and AI Deep Research for Sales Enrichment](/articles/ai-web-enrichment-for-sales.md): Deep research AI sales web enrichment using AI search APIs. Create custom prospect intelligence beyond Apollo/ZoomInfo with automated data gathering tools. ...``` The file acts as a curated guide specifically designed for AI consumption. When an AI agent visits your site, it can immediately locate your most valuable resources instead of wading through navigation menus, footers, and scattered content competing for limited token budget.
## **Why AI crawlers need a dedicated map**
AI systems face fundamentally different challenges than traditional search crawlers when processing web content. Search engines index keywords and follow link graphs, but LLMs need dense, contextual information to reason effectively. When an AI agent visits your website without guidance, it encounters navigation elements, advertisements, sidebars, and scattered content all at once.
The result? AI systems often miss your most valuable content or misinterpret what your site actually offers. They might focus on tangential blog posts while overlooking comprehensive documentation. They might struggle to understand how different sections relate to each other.
A well-structured llms.txt file eliminates this guesswork by explicitly stating what matters most and where to find it. Instead of forcing AI agents to infer structure from HTML, you're handing them a roadmap.
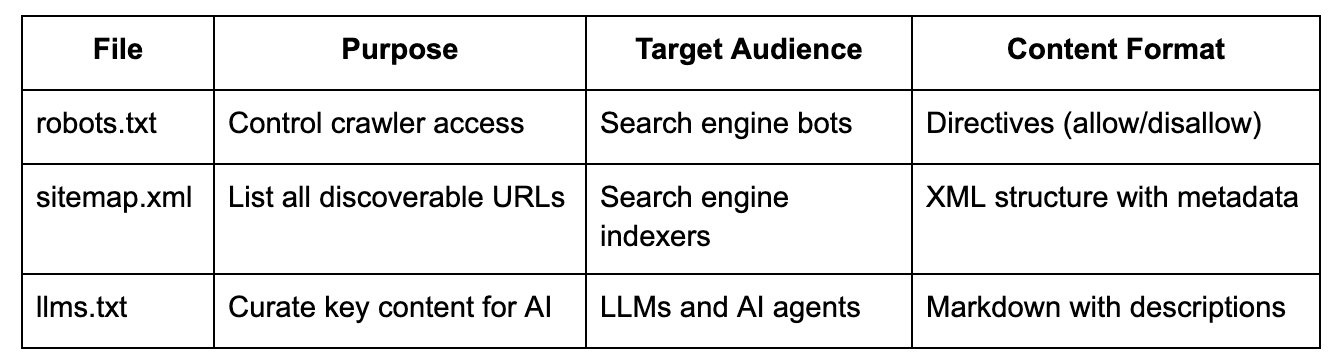
## **llms.txt vs Robots.txt vs Sitemap.xml**
You might be wondering how llms.txt differs from the other standard files websites use to communicate with automated systems. Each serves a distinct purpose:
While robots.txt tells crawlers what they _can't_ access and sitemap.xml tells them what _exists_, llms.txt tells AI systems what _matters_. It's a tool of inclusion rather than restriction—you're not blocking access, you're providing context that helps AI agents understand your content hierarchy.
## **llms.txt specification and format breakdown**
The llms.txt standard follows a specific markdown structure designed for clarity and consistency. At the top, you'll include an H1 heading with your site or project name, followed by a blockquote containing a concise description of what your organization does.
### **Required fields**
Every llms.txt file includes three core elements that form the foundation of the standard:
- - **Site name:** A clear identifier placed in an H1 heading
- - **Description:** A brief summary in blockquote format explaining your site's purpose
- - **URL structure:** Organized markdown sections with links and short descriptions for each important page
### **Optional metadata**
Beyond the basics, you can enhance your llms.txt file with additional context. Contact information, API documentation links, and specialized content sections help AI systems understand not just what you offer but how to engage with it. Some implementations include version numbers or last-updated timestamps to signal content freshness, though the core specification doesn't require them.
### **llms.txt standard examples**
The format prioritizes readability for both AI systems and humans who might review the file. Each link includes a description that explains what the page contains and why it matters, giving AI agents enough context to determine relevance without visiting every URL.
## **File locations for /llms.txt and /llms-full.txt**
The standard defines two complementary files that serve different purposes. The primary /llms.txt file contains your curated, high-level overview—think of it as an executive summary that points to your most important resources. This file typically remains concise, focusing on top-tier content that answers the most common questions about your site.
The optional /llms-full.txt file offers comprehensive coverage for AI systems that need deeper context. While llms.txt might link to 10-15 key pages, llms-full.txt can include your entire content inventory with detailed descriptions. Most implementations start with just the standard llms.txt file and add the full version later if needed.
## **Step-by-step creating an llms.txt file**
Building an effective llms.txt file starts with strategic thinking about what AI systems accessing your content actually need to know.
### **1. Decide which URLs to expose**
Start by identifying the pages that best represent your site's value. Documentation, core product pages, key blog posts, and essential resources typically make the cut. Avoid the temptation to include everything—curation matters more than comprehensiveness.
Ask yourself: if an AI agent could only access ten pages from your site, which would give it the most accurate understanding of what you offer? That's your starting point.
### **2. Write the markdown block**
Begin with your H1 site name, then add a blockquote description that captures your core value proposition in one or two sentences. Organize your links into logical sections using H2 headers—Documentation, Products, Resources, whatever structure makes sense for your content.
Each link includes a brief description explaining what the page contains. "API Reference" becomes "API Reference: Complete endpoint documentation with request/response examples." The extra context helps AI agents determine relevance without visiting every URL.
### **3. Upload to the site root**
Save your file as llms.txt and place it in your website's root directory, accessible at yourdomain.com/llms.txt. Most web servers serve static files from this location by default.
If you're using a content management system or static site generator, you might place the file in your public or static assets folder—wherever files go that are accessible at the domain root. The exact location varies by platform, but the goal remains the same: make the file available at the root URL.
### **4. Test with an llms.txt validator**
Several online validators, like https://llmtext.com/[https://llmtext.com/](https://llmtext.com/), can check your file's formatting and structure. The validators verify that your markdown follows the specification, your links are accessible, and your descriptions are clear. Testing catches common issues like broken links or malformed markdown before AI systems encounter them.
## **Validating and updating your llms.txt file**
Your llms.txt file isn't a set-it-and-forget-it asset. As your site evolves—new documentation launches, products change, content priorities shift—your llms.txt file changes with it.
Consider implementing a review cycle that aligns with your content publishing schedule. When you release major updates or new features, update your llms.txt file to reflect the changes. Version control systems like Git make it easy to track modifications over time.
## **Automating llms.txt generation in CI/CD pipelines**
For sites with frequently changing content, manual updates become impractical. Automated generation integrates llms.txt creation directly into your deployment workflow.
Scripts can scan your content management system, identify high-priority pages based on predefined rules, and generate properly formatted llms.txt files automatically. This approach works particularly well for documentation sites where content structure follows consistent patterns. You might write a script that pulls from your docs navigation, extracts page titles and descriptions from frontmatter, and outputs valid llms.txt markdown. The generated file then deploys alongside your content updates, staying perpetually synchronized.
## **Should you adopt llms.txt now?**
The llms.txt standard sits at an interesting inflection point. Major AI providers haven't officially committed to supporting the format, yet adoption continues growing among technical organizations and AI-focused companies.
Here's what favors early adoption: implementation costs remain minimal—you're creating a single text file. The potential upside includes better AI representation, more accurate citations, and improved discoverability for AI-powered tools. Even without universal support, some systems already consume the files, and the trend points toward increasing adoption.
The main consideration? Opportunity cost. If creating and maintaining an llms.txt file takes an hour, and there's even a modest chance it improves how AI systems represent your content, the expected value calculation favors implementation.
## **Common mistakes and how to avoid them**
Three issues consistently trip up first-time llms.txt implementers:
- - **Incomplete descriptions:** Vague phrases like "Learn more" or "Product page" don't help AI systems understand what content actually contains—be specific about what each link offers
- - **Broken links:** URLs that redirect, return 404s, or require authentication create dead ends for AI agents—validate every link before publishing
- - **Poor organization:** Dumping links without logical grouping makes the file harder to parse—use clear section headers that reflect content categories
Regular audits catch problems before they impact AI system performance. Treat your llms.txt file with the same quality standards you'd apply to public-facing documentation.
## **The path forward for AI-friendly web content**
The llms.txt standard represents something larger than a single file format. It signals a fundamental shift in how we think about web content accessibility.
As AI agents become primary consumers of web information alongside humans, content creators need new tools to communicate structure, priority, and context. We're likely to see the standard evolve—future versions might include semantic markup for different content types, versioning information, or integration with other structured data formats.
The core principle remains constant: giving AI systems explicit guidance produces better outcomes than forcing them to infer structure from HTML.
Ready to build AI agents that leverage structured web content? Start building[Start building](https://platform.parallel.ai/home) with Parallel's APIs designed for reliable, high-accuracy information retrieval from the open web.
## FAQs About llms.txt
### Does llms.txt affect Google search rankings?
The llms.txt file doesn't directly impact traditional SEO rankings since it's designed for AI systems, not search engine crawlers. Google's indexing algorithms focus on factors like content quality, backlinks, and technical SEO—none of which llms.txt influences. However, better AI representation might indirectly benefit your visibility as AI-powered search tools gain prominence.
### How large can an llms.txt file become?
There's no strict size limit, but keep files focused and manageable—typically under a few hundred links with concise descriptions for optimal AI processing. Remember that LLMs have context window constraints, and extremely large files might get truncated during processing. If you need comprehensive coverage, consider using the llms-full.txt extension for detailed content while keeping your primary llms.txt file lean.
### Can I restrict specific AI providers from accessing my llms.txt?
The current specification doesn't include provider-specific restrictions, though you can control access through standard web server configurations and robots.txt directives. If you want certain AI systems to access your content while blocking others, you'll rely on existing web access control mechanisms rather than llms.txt-specific features. The file itself is designed as an inclusive tool for any AI system that chooses to respect it.
By Parallel
October 25, 2025